Table of Contents
Assisting those rescued from water in hypothermic conditions
Remember that timely notification of an accident is a decisive factor in saving life! Emergency services take care of accidents at sea:
- Phone 115 (emergency service).
- The emergency telephone number of the State Fire and Rescue Service is 112.
If a person suffers from hypothermia (hypothermia), he begins to tremble, most people also have difficulty moving - they become slower and lose coordination. Under the influence of hypothermia, a person can also feel dazed, confused, lost the ability to navigate in space. Hypothermia may also impair the individual's ability to speak and may appear to the outside to be under the influence of alcohol or other drugs.
In the case of very strong hypothermia, breathing can already become difficult and the heart rate can reach a critically low level - in this condition, a person first loses consciousness and eventually freezes. At the same time, there are known cases when a person manages to perform various strange actions in the last moments before freezing, which, according to scientists, could be the brain's last attempt to save life.
Learn more about surviving hypothermia
- Abandoning the watercraft and ship in an emergency
- Human survival in the sea, cold water in autumn and winter
- The benefits of a cold bath are why you need to do it
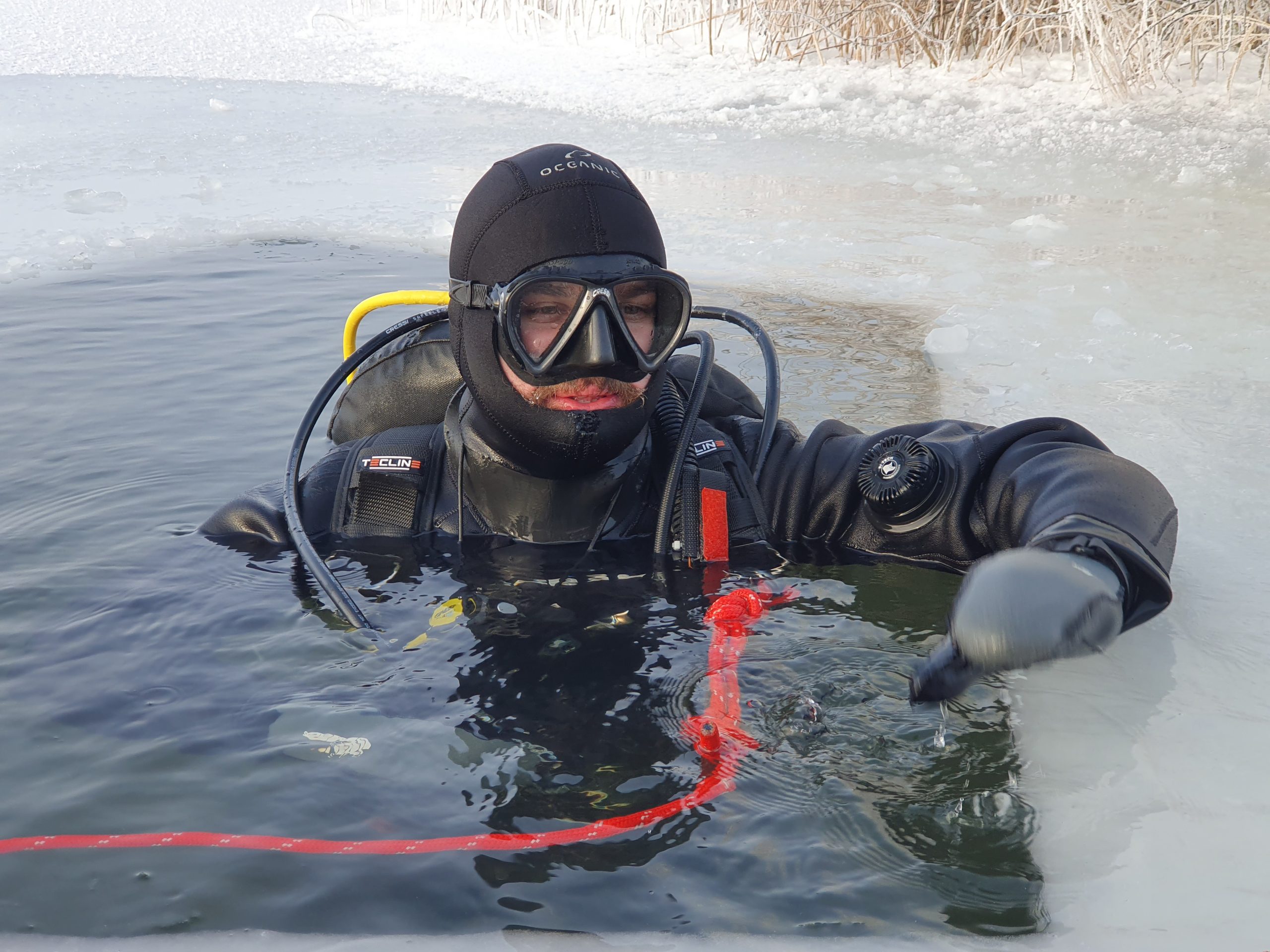
- Diving in autumn and winter in Latvian waters
- Motivational technique for a cold winter swim
Providing assistance hypothermia in case, of course, will depend on the general condition of the survivor and the resources available to the rescuers. Usually, rescuers who are sane and able to remember what they experienced, even though they are shaking violently, need only remove all wet clothing and replace them with dry clothing or blankets. If there are no warm clothes or blankets and if it is not possible to take off the wet clothes, the victim can be wrapped in polyethylene film or placed in a polythene bag with all the wet clothes, so the victim will lose much less heat. Victims should be lifted out of the water in the most horizontal position possible and also carried in this way or sooner placed lying down. Even better – in a position in which the person is placed unconscious, and should be left there until further assistance.
Hot and sweet drinks may be given to the victim only if the person is conscious and has a gagging and coughing reflex. It is also recommended to rest in heat that does not exceed +25 °C (room temperature). Do not drink alcohol or smoke. The cooled skin should not be massaged or rubbed.
It should always be kept in mind that rescuers who are initially conscious may become ill and lose consciousness soon after rescue. Therefore, they should be placed lying down with their legs slightly raised (shock position) and continuously monitored until the body temperature reaches +35 °C. In more severe cases, when the rescued person does not shake and is partially or completely unconscious or does not have any signs of life at all, it is necessary to provide emergency aid to save life while waiting for the doctor's instructions for specific assistance measures. You should see a doctor as soon as possible, and emergency measures should not be stopped until the doctor arrives.
Emergency measures after pulling out of the water, if the victim is unconscious after being rescued:
1. Frees the victim's airways:
- examines and, if necessary, cleans the oral cavity (well-fixed dentures are left, but if they are loose, they are removed),
- tilt the victim's head back and pull the lower jaw forward with a quick movement;
2. If the rescued person is not breathing, immediately start artificial respiration (from mouth to mouth or from mouth to nose) with two exhalations of the rescuer in the victim's airways;
3. Controls the air circulation for 10 seconds, observes whether the victim does not cough or does not move the chest or other parts of the body;
4. If air circulates, artificial respiration continues 12 times per minute (once in 5 seconds). Signs of air circulation should be checked every minute. If they are not present, start artificial heart massage (ratio of breathing and heart massage is 2:15). Once CPR is started, it should be continued until the patient is fully rewarmed or transported to the hospital;
5. If the rescued person is breathing but is unconscious, place him in a stable side-lying position. This is necessary to ensure that the person's airways are not blocked by the tongue or vomit;
6. Unnecessary moving of the victim should be avoided, for example, to check for serious injuries, do not remove wet clothes. Do not massage the victim;
7. Further heat loss due to wind and water evaporation should be prevented. Carefully wrap the victim in a blanket and/or rescue bag or a large plastic bag and immediately move him to a leeward or room where the air temperature reaches normal room temperature. The victim is placed in a horizontal position, head slightly down;
8. Advice on warming up victims and decisions on further treatment should be obtained from a doctor. If a doctor's advice is not immediately available, the life-saving procedures mentioned in points 1-5 should be continued. in point If the condition of the person pulled out of the water worsens – breathing stops and the pulse disappears – or he looks as if he is dead, resuscitation should not be stopped until the victim has warmed up. The best method of active warming is to keep a warm blanket under the victim, but not warmer than +40 °C. The victim should not be warmed in the bath or shower. Do not try to warm the person by vigorously moving their arms or legs. Never put warm objects near exposed skin, as frostbitten skin can be easily burned.
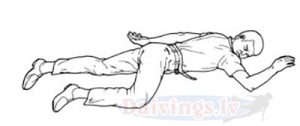
The safest position for an unconscious person is to lay him on his stomach, turning his head to the side. Don't put a pillow under your head. Pull up the leg that is on the side to which the head is turned, and put the arm of the same side in a bent position forward. The chin is pulled up. The other arm is straightened as shown in the drawing. Clothes should be loose around the neck and waist. Dentures must be removed.
In conclusion about hypothermia and cold therapy
Deliberately walking into cold water can take a lot of getting used to, but the benefits of an ice bath and how you feel afterward are worth it. An improved immune system, better mental clarity and health, and an improved metabolism are pretty tempting benefits and reasons why it's worth pursuing.

More about tempering, ice and cold baths
Cold water shower, hardening benefits
The benefits of a cold bath are why you need to do it
Motivational technique for a cold winter swim
Where to apply for diving training in Latvia?
🤿😀 If you are looking for diving advice or advice on the sport of scuba diving with or without balloons, call a PADI Diver Instructor (PADI diving instructor and lecturer Valters Preimanis) t. 220-77-202 (WhatsApp 220-77-202).

